NVR - Codes

In your 11+ NVR assessment, you might be required to examine a mix of shapes and symbols, each accompanied by specific code letters that describe them.
Using the patterns of these shapes and codes, you may need to identify either the shape corresponding to a code or the code that represents a shape.
NVR - Codes
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF
We can't really deduce much from this combination of shapes and letters. We can guess that perhaps the A represents the square and F represents the pentagon, but we don't really have enough information.
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF
With more samples to analyse, however, we can start working out a logical pattern.
We notice that every shape with a pentagon has an F, every shape with a circle has a G and every shape with a square has an A.


GF
GA
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF
With more samples to analyse, however, we can start working out a logical pattern.
We notice that every shape with a pentagon has an F, every shape with a circle has a G and every shape with a square has an A.


GF
GA


Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF
With more samples to analyse, however, we can start working out a logical pattern.
We notice that every shape with a pentagon has an F, every shape with a circle has a G and every shape with a square has an A.


GF
GA


Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF
With more samples to analyse, however, we can start working out a logical pattern.
We notice that every shape with a pentagon has an F, every shape with a circle has a G and every shape with a square has an A.


GF
GA


Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF
We can even make a reasonable prediction about the order of the letters:
The first letter seems to refer to the outer shape, the second letter seems to refer to the inner shape.


GF
GA
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF


GF
GA

? ?
Text
Given our earlier conclusions, we can solve a question like this quite easily:
The first letter should be an F, representing a pentagon
The second letter should be a G, representing a circle.
F
G
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF


GF
GA

? ?
Text
Given our earlier conclusions, we can solve a question like this quite easily:
The first letter should be an F, representing a pentagon
The second letter should be a G, representing a circle.
F
G
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF


GF
GA
GG
Text
You may also see the question presented like this. Now you have the code, and you must choose the matching shape.





Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

AF


GF
GA
GG
Text
Knowing that the letter G represents a circle, the code GG would represent a circle within a circle.





Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
As you have seen, codes can represent shapes. But they can also represent other attributes of an object, such as colour, shading, position etc.
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
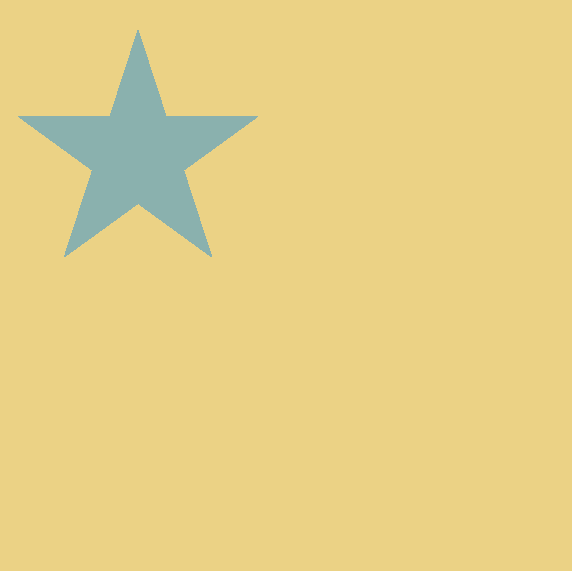
MFT
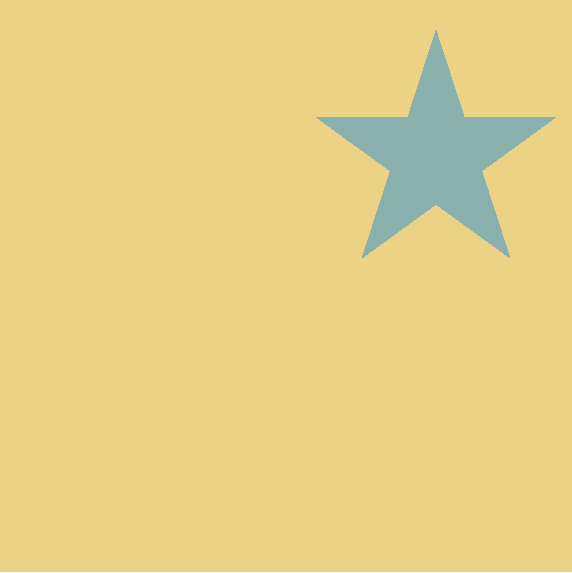
MFZ
USZ
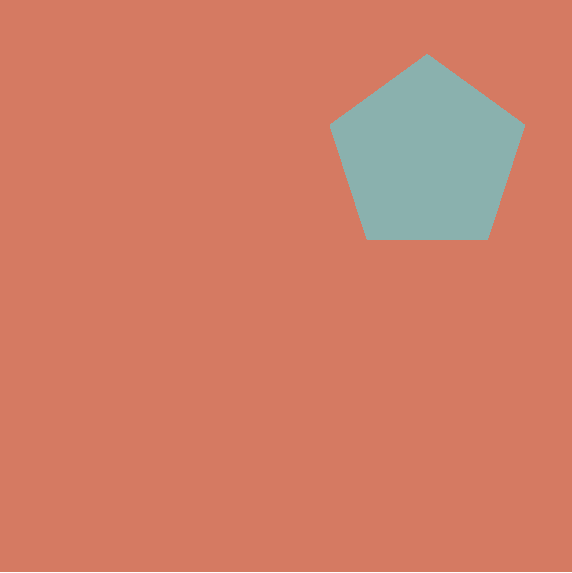

UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.
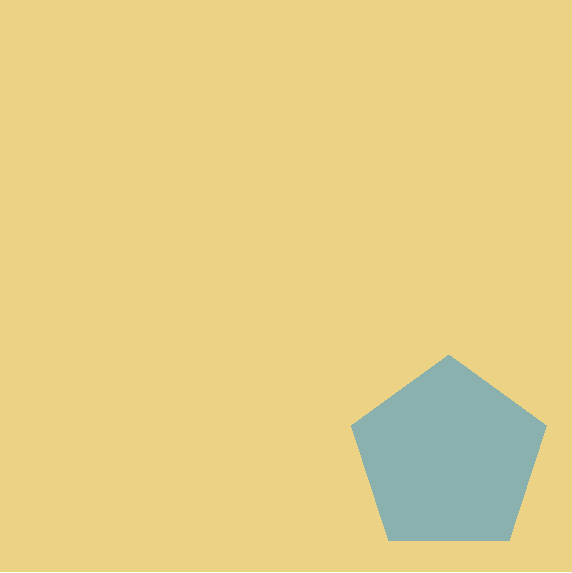
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

Questions like this may at first seem overwhelming. The trick is to break the code step-by-step. Let's look at the closely at the shapes and codes.
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

What does the two yellow boxes all have in common?
They share M and F.
M=yellow box
U=red box
F=star
S=pentagon
T=top left
Z=top right
G=bottom right
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

What does the two yellow boxes all have in common?
They share M and F.
But the 4th box is red and also has an F.
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

What does the two yellow boxes all have in common?
They share M and F.
But the 4th box is red and also has an F.
It's reasonable to presume for now that an M represent yellow.
yellow.
M
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

The two red shapes share only the colour. One has a pentagon and one has a star. They only share the letter U. For now, we can presume that U represent the colour red.
yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
red
U
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

We have already decoded the colour part of the question. Now, let's see if we can decipher the rest of the letters.
M = yellow
red
U
U = red
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

Which letter is common for shapes containing a star?
yellow.
F
M = yellow
Every shape that features a star contains the letter F in its code. None of the other shapes include this letter.
This leads us to conclude that F represents star.
star
F
U = red
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

Which letter is common for shapes containing a star?
yellow.
F
M = yellow
Every shape that features a star contains the letter F in its code. None of the other shapes include this letter.
This leads us to conclude that F represents star.
star
F
F = star
U = red
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

The second and third shape both share the letter Z. But they share neither the colour nor the shape: one is a yellow box with a star, the other is a red box with a pentagon.
yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
Which other feature do they share? Well, they both have the object in the top right-hand corner. They are the only shapes with the inner object in that position, and the only shapes with Z in the code.
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
Let's presume for now that a Z means top-right-hand corner.
top-right-hand corner
Z
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
Let's presume for now that a Z means top-right-hand corner.
top-right-hand corner
Z
Z = top-right position
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
We can now make some reasonable guesses about the remaining letters. If Z represents the top-right, then T likely indicates the top-left, and G would correspond to the bottom-right.
top-right-hand corner
Z
Z = top-right position
T likely indicates the top-left
G would correspond to the bottom-right
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
The only letter not yet decoded is S. As we know what U and Z means, S is likely the code for a pentagon.
top-right-hand corner
Z
Z = top-right position
T likely indicates the top-left
G would correspond to the bottom-right
T = top-left position
G = bottom-right position
pentagon.
S
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
We can now generate a code to match the last shape:
top-right-hand corner
Z
Z = top-right position
T likely indicates the top-left
G would correspond to the bottom-right
T = top-left position
G = bottom-right position
pentagon.
S
S = pentagon
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
We can now generate a code to match the last shape:
top-right-hand corner
Z
Z = top-right position
T likely indicates the top-left
G would correspond to the bottom-right
T = top-left position
G = bottom-right position
pentagon.
S
S = pentagon
M for yellow
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
We can now generate a code to match the last shape:
top-right-hand corner
Z
Z = top-right position
T likely indicates the top-left
G would correspond to the bottom-right
T = top-left position
G = bottom-right position
pentagon.
S
S = pentagon
M for yellow
G for bottom-right
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
We can now generate a code to match the last shape:
top-right-hand corner
Z
Z = top-right position
T likely indicates the top-left
G would correspond to the bottom-right
T = top-left position
G = bottom-right position
pentagon.
S
S = pentagon
M for yellow
G for bottom-right
S for pentagon
M
G
S
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes

MFT

MFZ
USZ


UFG
Find the missing letter code for the last object.

yellow.
F
M = yellow
star
F
F = star
U = red
We can now generate a code to match the last shape:
top-right-hand corner
Z
Z = top-right position
T likely indicates the top-left
G would correspond to the bottom-right
T = top-left position
G = bottom-right position
pentagon.
S
S = pentagon
M for yellow
G for bottom-right
S for pentagon
M
G
S
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
In the examples so far, there has been no unknown letters in the final code.
For your 11+ NVR assessment, however, you may occasionally come across questions where you must use a process of elimination to decipher letters not used elsewhere.
Let's look at an example.
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
BL
SL
SF
BF





Select the code to match the last shape
Text
BL
TF
SF
TL
TO
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
BL
SL
SF
BF





Select the code to match the last shape
Text
BL
TF
SF
TL
TO
Using the logic from past questions we can decipher the likely meaning of some letters:
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
BL
SL
SF
BF





Select the code to match the last shape
Text
BL
TF
SF
TL
TO
Using the logic from past questions we can decipher the likely meaning of some letters:
B = blue triangle
L = orange hexagon
S = green triangle
F = red pentagon
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
BL
SL
SF
BF





Select the code to match the last shape
Text
BL
TF
SF
TL
TO
Using the logic from past questions we can decipher the likely meaning of some letters:
B = blue triangle
L = orange hexagon
S = green triangle
F = red pentagon
? = purple triangle
There are no other shapes containing a purple triangle, so we cannot say which letter represent that.
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
BL
SL
SF
BF





Select the code to match the last shape
Text
BL
TF
SF
TL
TO
Using the logic from past questions we can decipher the likely meaning of some letters:
B = blue triangle
L = orange hexagon
S = green triangle
F = red pentagon
? = purple triangle
But we know the final code will contain the letter L (orange hexagon) and none of the letters B, S or F (as they represent shapes not present in the last shape).
Let's look at some examples.
NVR - Codes
BL
SL
SF
BF





Select the code to match the last shape
Text
Using the logic from past questions we can decipher the likely meaning of some letters:
B = blue triangle
L = orange hexagon
S = green triangle
F = red pentagon
? = purple triangle
But we know the final code will contain the letter L (orange hexagon) and none of the letters B, S or F (as they represent shapes not present in the last shape).
Only option d meets those criteria. T must mean "purple triangle" and answer d must be the correct answer.
BL
TF
SF
TL
TO
NVR - Codes
Hints and tips for NVR shape codes
Look for Patterns and Rules: Pay attention to how shapes, numbers, or letters change across the sequence. Changes in size, rotation, colour, or position often follow a logical rule.
Break Down Complex Codes: Separate different elements (e.g., numbers, shapes, or symbols) and analyze them individually. This can make it easier to spot hidden patterns.
Eliminate Wrong Options: If you’re unsure, rule out clearly incorrect answers. Focus on the options that fit some or most of the observed patterns.
Think Logically, Not Randomly: Codes are always based on logic, so avoid making guesses without analysis. Look for clues like sequences, pairings, or repetitions.
Check Your Work: After identifying a possible answer, go back and verify it against all parts of the code. Ensure it satisfies every aspect of the pattern or rule.
NVR - Codes
Hints and tips for NVR shape codes
Look for Patterns and Rules: Pay attention to how shapes, numbers, or letters change across the sequence. Changes in size, rotation, colour, or position often follow a logical rule.
Break Down Complex Codes: Separate different elements (e.g., numbers, shapes, or symbols) and analyze them individually. This can make it easier to spot hidden patterns.
Eliminate Wrong Options: If you’re unsure, rule out clearly incorrect answers. Focus on the options that fit some or most of the observed patterns.
Think Logically, Not Randomly: Codes are always based on logic, so avoid making guesses without analysis. Look for clues like sequences, pairings, or repetitions.
Check Your Work: After identifying a possible answer, go back and verify it against all parts of the code. Ensure it satisfies every aspect of the pattern or rule.
NVR - Codes
Hints and tips for NVR shape codes
Look for Patterns and Rules: Pay attention to how shapes, numbers, or letters change across the sequence. Changes in size, rotation, colour, or position often follow a logical rule.
Break Down Complex Codes: Separate different elements (e.g., numbers, shapes, or symbols) and analyze them individually. This can make it easier to spot hidden patterns.
Eliminate Wrong Options: If you’re unsure, rule out clearly incorrect answers. Focus on the options that fit some or most of the observed patterns.
Think Logically, Not Randomly: Codes are always based on logic, so avoid making guesses without analysis. Look for clues like sequences, pairings, or repetitions.
Check Your Work: After identifying a possible answer, go back and verify it against all parts of the code. Ensure it satisfies every aspect of the pattern or rule.
NVR - Codes
Hints and tips for NVR shape codes
Look for Patterns and Rules: Pay attention to how shapes, numbers, or letters change across the sequence. Changes in size, rotation, colour, or position often follow a logical rule.
Break Down Complex Codes: Separate different elements (e.g., numbers, shapes, or symbols) and analyze them individually. This can make it easier to spot hidden patterns.
Eliminate Wrong Options: If you’re unsure, rule out clearly incorrect answers. Focus on the options that fit some or most of the observed patterns.
Think Logically, Not Randomly: Codes are always based on logic, so avoid making guesses without analysis. Look for clues like sequences, pairings, or repetitions.
Check Your Work: After identifying a possible answer, go back and verify it against all parts of the code. Ensure it satisfies every aspect of the pattern or rule.
NVR - Codes
Hints and tips for NVR shape codes
Look for Patterns and Rules: Pay attention to how shapes, numbers, or letters change across the sequence. Changes in size, rotation, colour, or position often follow a logical rule.
Break Down Complex Codes: Separate different elements (e.g., numbers, shapes, or symbols) and analyze them individually. This can make it easier to spot hidden patterns.
Eliminate Wrong Options: If you’re unsure, rule out clearly incorrect answers. Focus on the options that fit some or most of the observed patterns.
Think Logically, Not Randomly: Codes are always based on logic, so avoid making guesses without analysis. Look for clues like sequences, pairings, or repetitions.
Check Your Work: After identifying a possible answer, go back and verify it against all parts of the code. Ensure it satisfies every aspect of the pattern or rule.

Well done! You should now have a very good understanding of codes in non-verbal reasoning. NVR requires a lot of practice, however, so the next step is to get going with some of our NVR mock tests. Don't despair if your first scores aren't as good as you had hoped. The key to NVR tests is familiarity with the question types. Keep practicing and you will notice that you get a little bit better and a little bit faster each time.