Similarities and Pattern Identification
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
A 3D shape is an object that has length, width, and height. This is different from flat 2D shapes like circles or squares:
2D
3D
A 3D shape has volume and exists in three-dimensional space, allowing it to be viewed from different angles. 3D shapes are the building blocks of the real world.
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
A 3D shape is an object that has length, width, and height. This is different from flat 2D shapes like circles or squares:


2D
3D
Area
Volume
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
A 3D shape is an object that has length, width, and height. This is different from flat 2D shapes like circles or squares:


2D
3D
Area
Volume
cm
cm
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
Overview of Common 3D Shapes


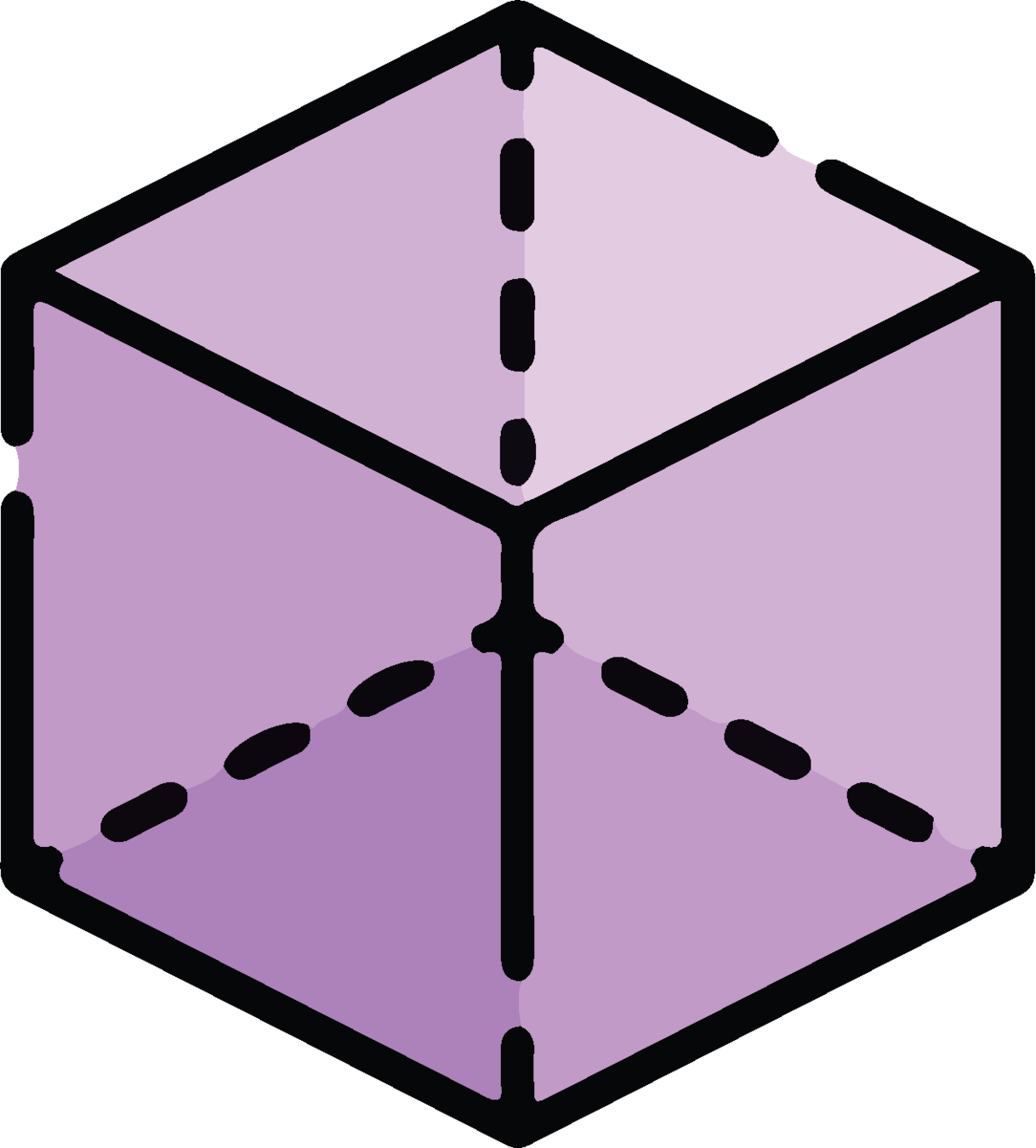
Cylinder
Cone
Cube

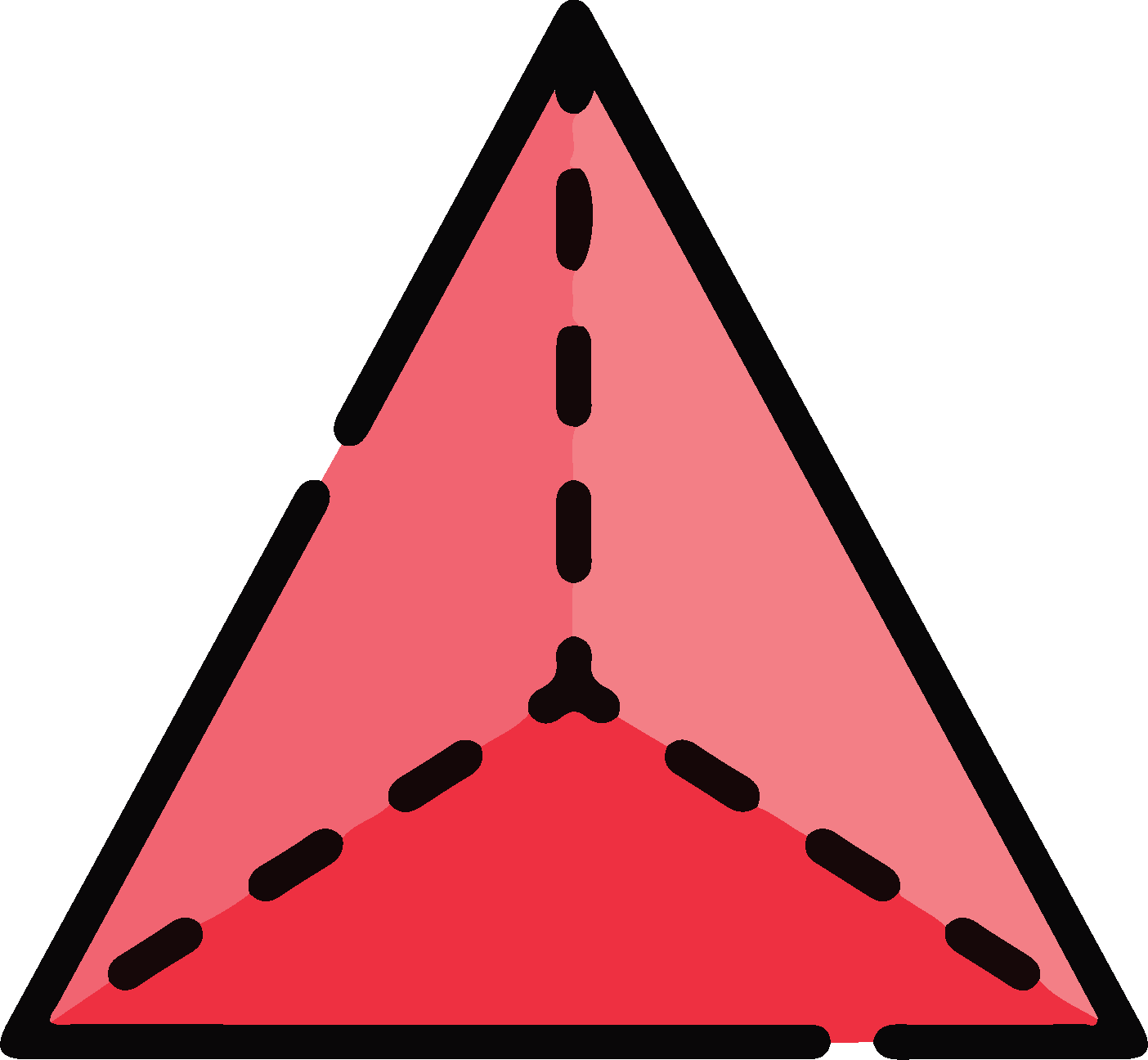

Sphere
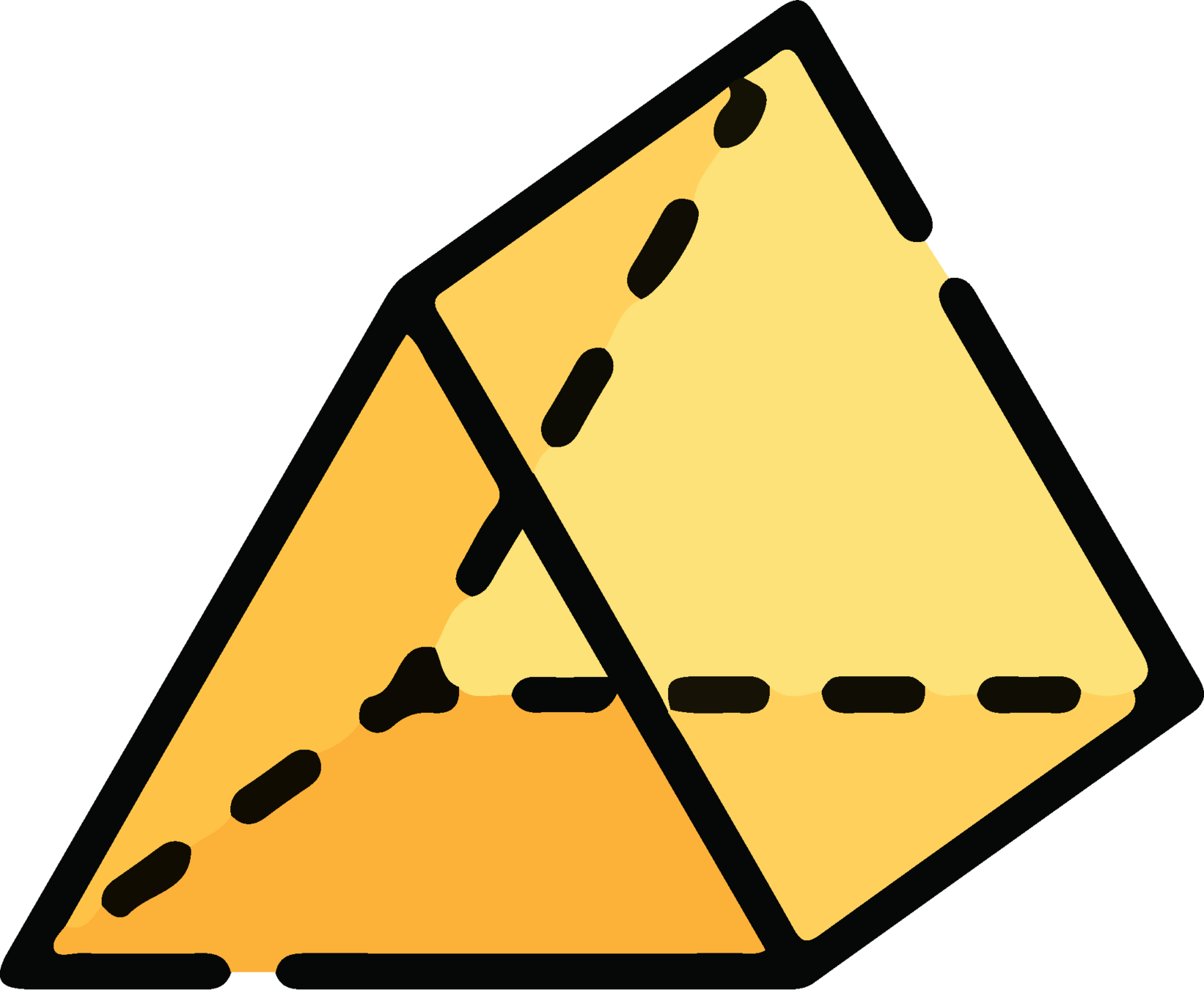
Tetrahedron
Square pyramid
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
Overview of Common 3D Shapes



Cylinder
Cone
Cube



Sphere
Tetrahedron
Square pyramid
Pentagonal pyramid
Octahedron
Dodeca-hedron
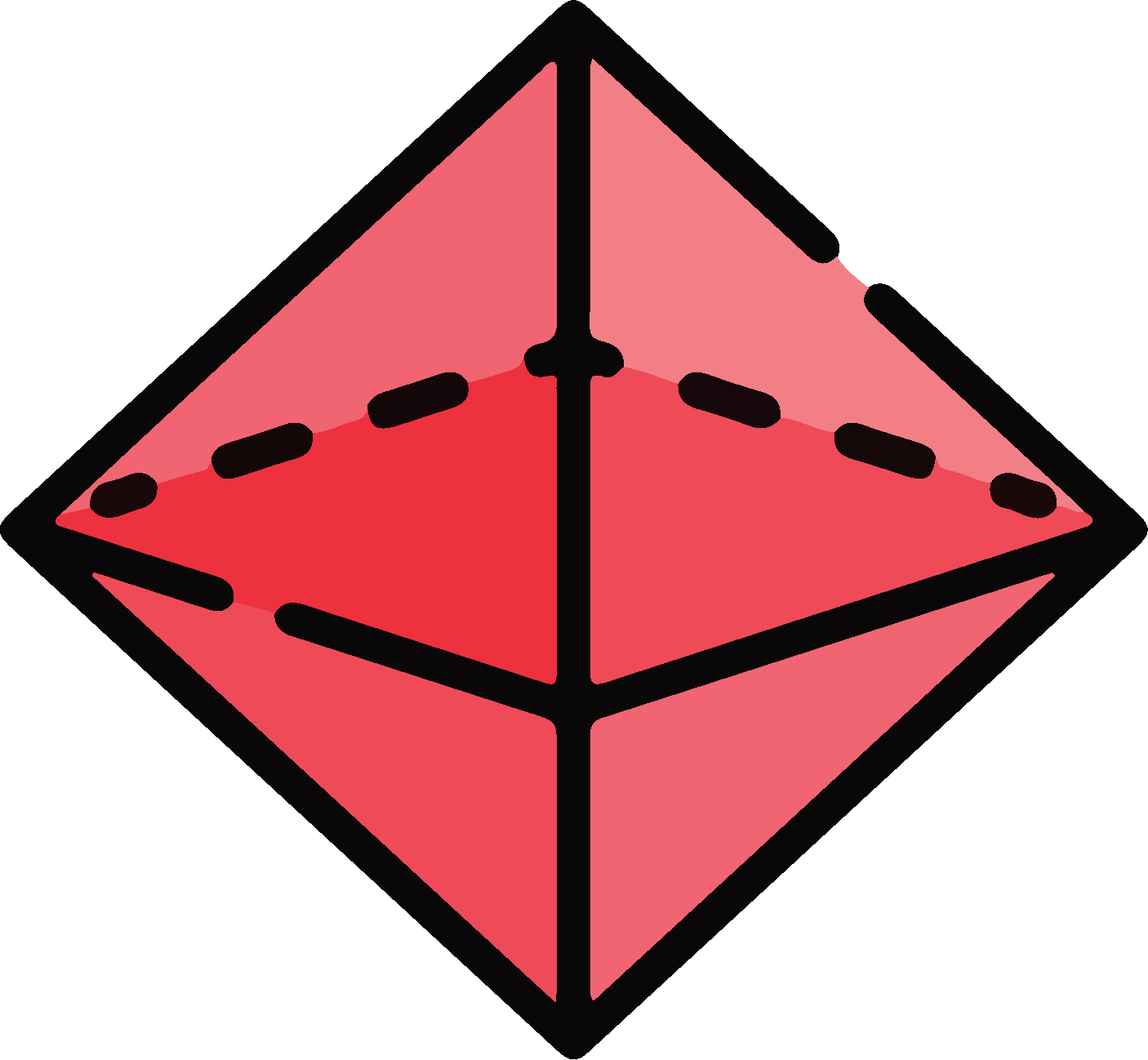


3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
Overview of Common 3D Shapes



Sphere
Tetrahedron
Square pyramid
Pentagonal pyramid
Octahedron
Dodeca-hedron



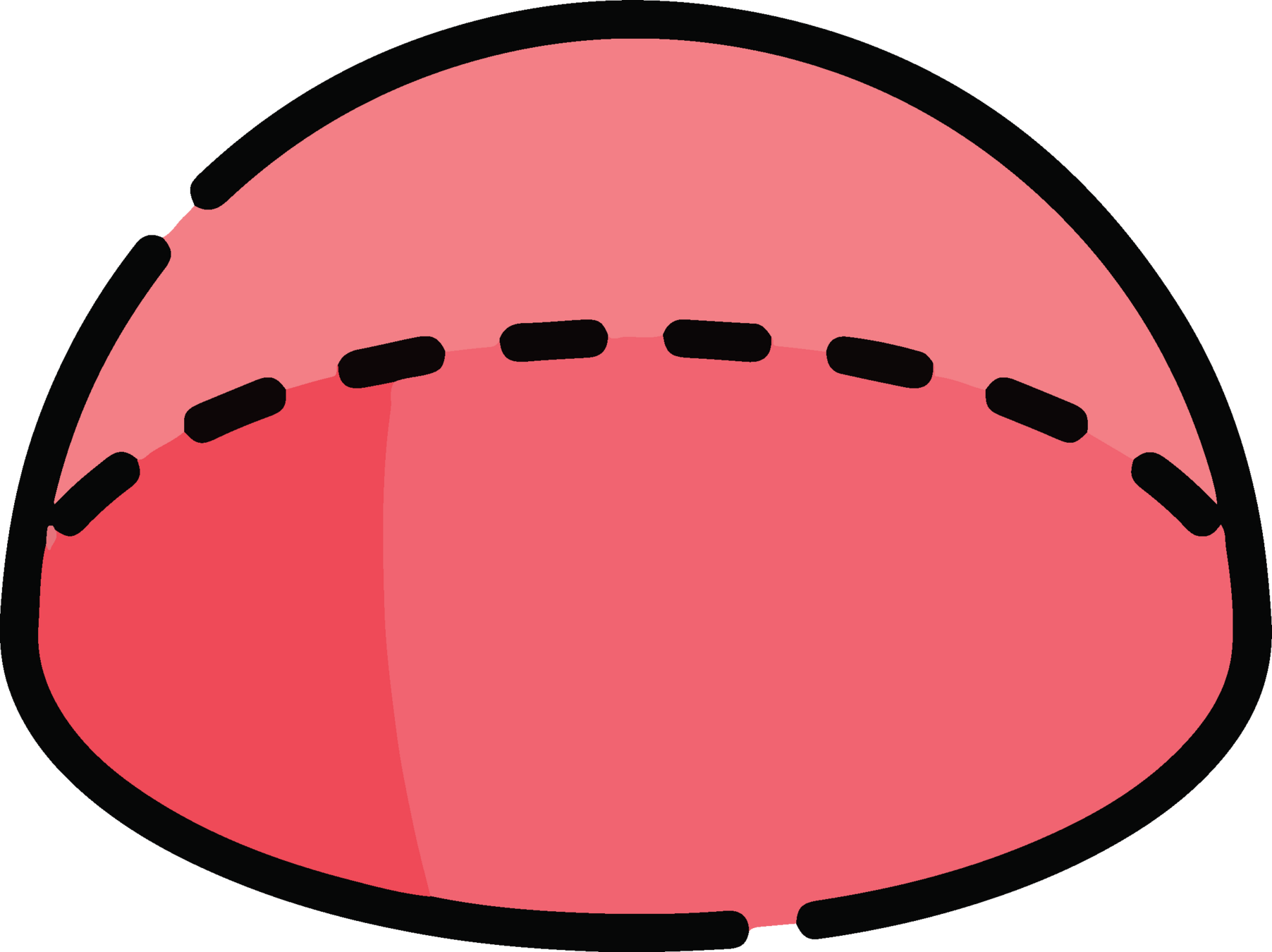
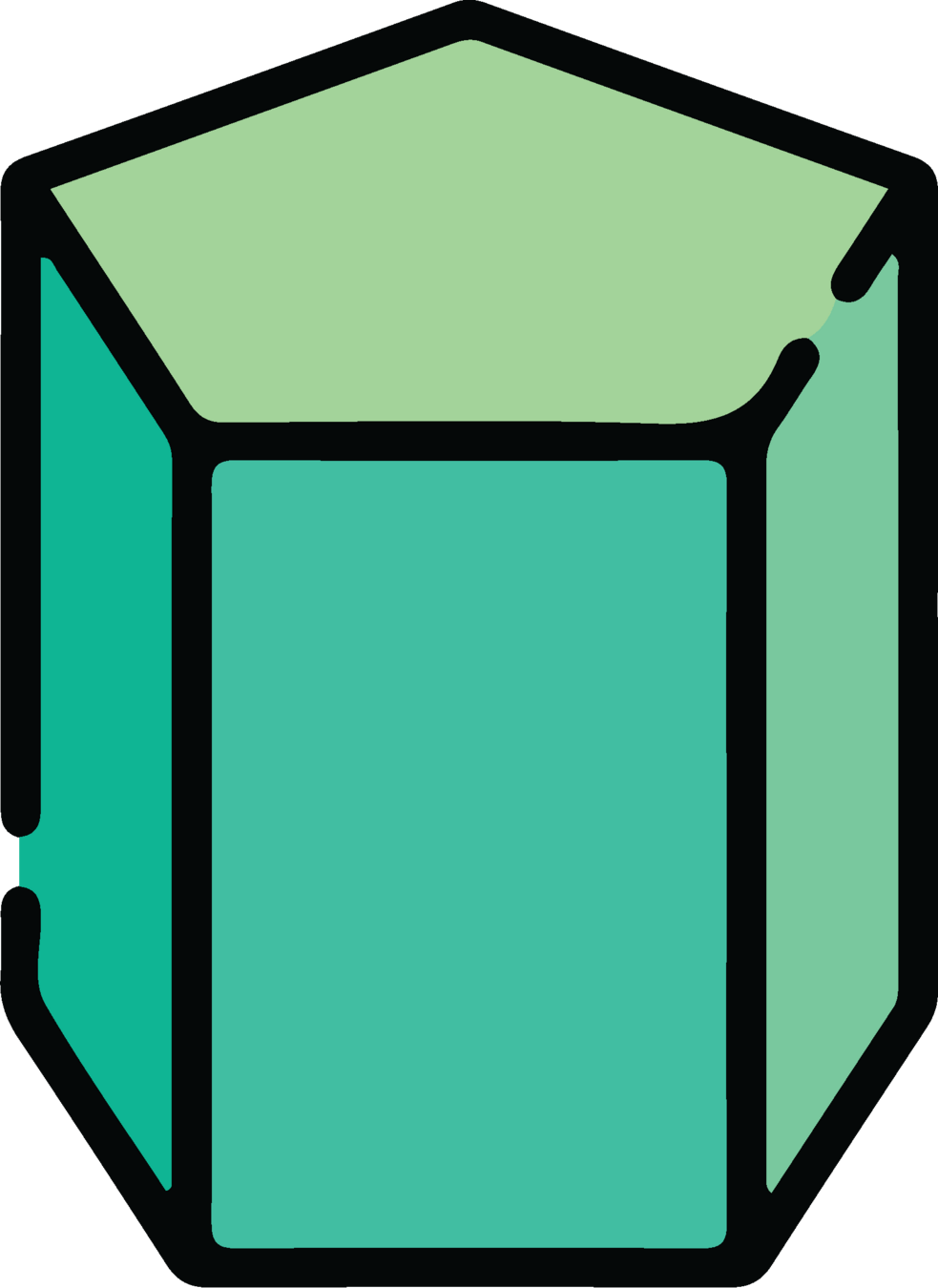
Semisphere
Pentagonal prism
Triangular prism
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
Overview of Common 3D Shapes
Pentagonal pyramid
Octahedron
Dodeca-hedron






Semisphere
Pentagonal prism
Triangular prism
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations
For your 11+, you may be asked to identify 3D shapes and thus it is worth learning the names of these.



Semisphere
Pentagonal prism
Triangular prism


Pentagonal pyramid
Octahedron
Dodeca-hedron




Sphere
Tetrahedron
Square pyramid



Cylinder
Cone
Cube
3D Shapes and 3D Rotations



Semisphere
Pentagonal prism
Triangular prism


Pentagonal pyramid
Octahedron
Dodeca-hedron




Sphere
Tetrahedron
Square pyramid



Cylinder
Cone
Cube
As you will notice, most of the names are logical and based on 2D shapes you already know.
"Dodeca" is Greek for 12. This 3D object has 12 sides.
3D Rotations
In your 11+ exam, you may encounter questions about 3D rotations.
These questions typically present a 3D shape in one orientation, and you'll need to identify the same shape in a different orientation.
3D Rotations
Study this shape
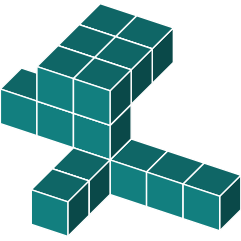
3D Rotations
Study this shape

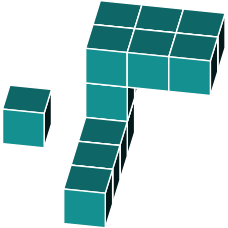
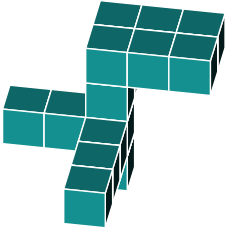
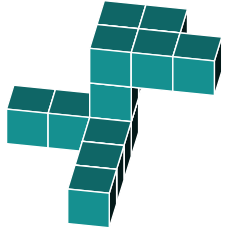
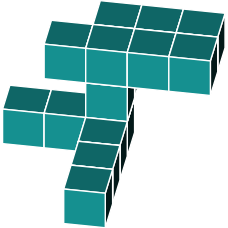
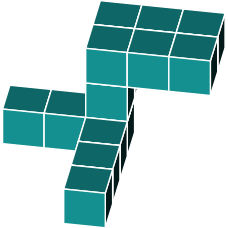
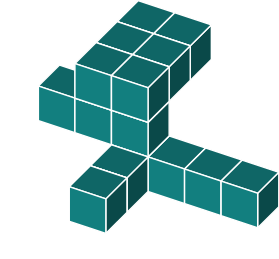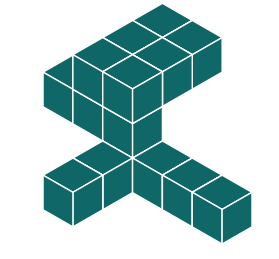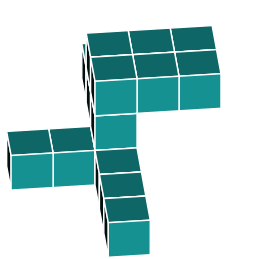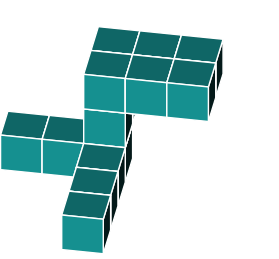
Identify the same shape from the alternatives below
3D Rotations
Study this shape






First, we need to determine how the figure has been rotated. The most recognizable feature in the original is the large 2x3 block at the top.
3D Rotations
Study this shape






We can identify the same 2x3 block in the shapes shown below.
3D Rotations
Study this shape






By examining the protruding blocks, we can determine the block's rotation.
3D Rotations
Study this shape






In figure a, we notice that a block is missing. Therefore, we can eliminate this option.
3D Rotations
Study this shape






Figure b seems to be a better match. However, upon closer inspection, we notice an additional block at the bottom. When comparing it to the original, we see that this block is absent. Therefore, we can rule out b.
3D Rotations
Study this shape






In figure c we quickly spot a missing block in the top 3x2 rectangle. We can rule out option c.
3D Rotations
Study this shape






In figure d we find an additional block on one side of the 3x2 rectangle. We can rule out option d.
3D Rotations
Study this shape






This brings us to option e. Studying it carefully, it appears to be an exact rotation of the original shape.
The correct answer is e.
3D Rotations
Study this shape







3D Rotations
Study this shape
In the previous question, the shape was rotated in just one direction. Now, let's explore a shape that is rotated around two axes.
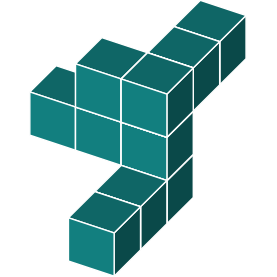
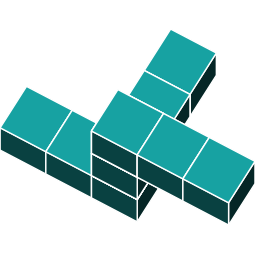
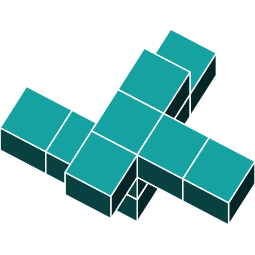
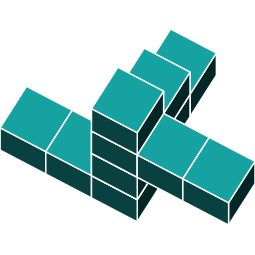
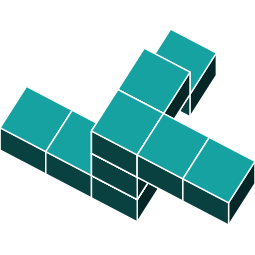
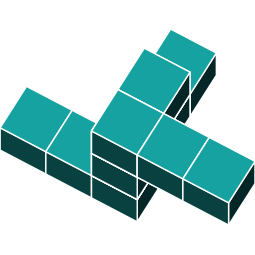
3D Rotations
Study this shape
In the previous question, the shape was rotated in just one direction. Now, let's explore a shape that is rotated around two axes.

By identifying the orientations of the main features, you can see that the object has been rotated around two axes.





3D Rotations
Study this shape

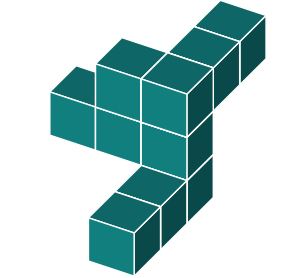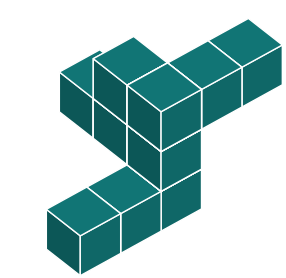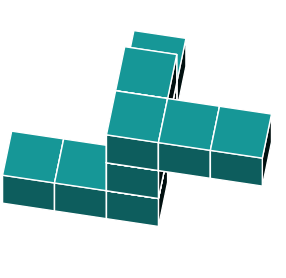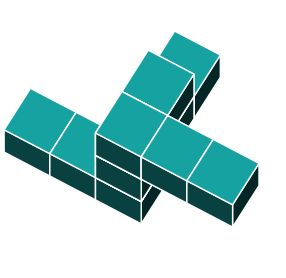
Can you identify which of these shapes is an exact rotation of the original shape?





3D Rotations
Study this shape

Shape e has an additional block on the side. We can rule out this shape.





3D Rotations
Study this shape

Shape d has an additional block at the top. We can rule out this shape.





3D Rotations
Study this shape

Shape c is missing a block at the bottom. We can rule out this answer alternative.





3D Rotations
Study this shape

Shape b is missing a block on top. We can rule out this answer alternative.





3D Rotations
Study this shape

Shape a is the only shape that is an exact rotation of the original.





3D Rotations
Study this shape

Shape a is the only shape that is an exact rotation of the original.






3D Rotations
A distinctive form of rotation takes place when a 3D object is oriented to resemble a 2D object.
This occurs when either the original orientation or the final orientation aligns perfectly on a flat plane, obscuring all sides.
3D Rotations
A distinctive form of rotation takes place when a 3D object is oriented to resemble a 2D object.
This occurs when either the original orientation or the final orientation aligns perfectly on a flat plane, obscuring all sides.
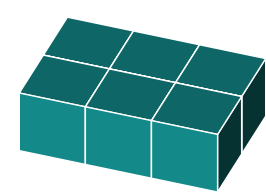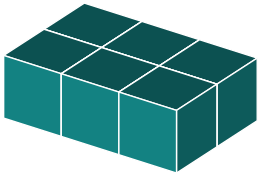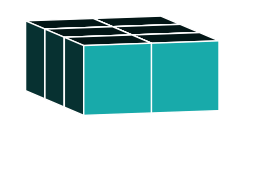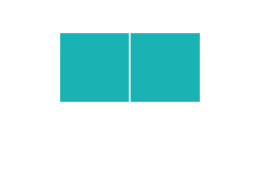
3D Rotations
Study this shape
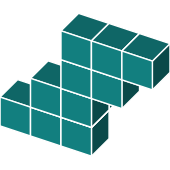
3D Rotations
Study this shape

Now select the image that is a rotation of the shape above
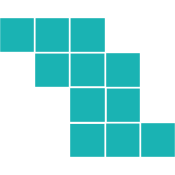
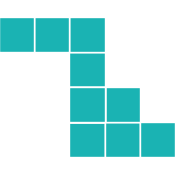
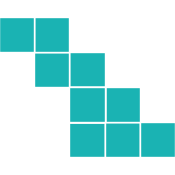
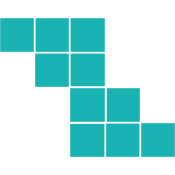
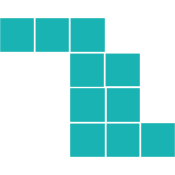
3D Rotations





Again, it makes sense to start by understanding the rotation.
The original shape has the top three blocks protruding to the right of the middle.
Likewise, the bottom three blocks protrude to the left of the middle.

3D Rotations





Likewise, the bottom three blocks protrude to the left of the middle.
We can easily visualize the shape based on this information. When we compare it to the available options, we see that the main features are reversed.
Text
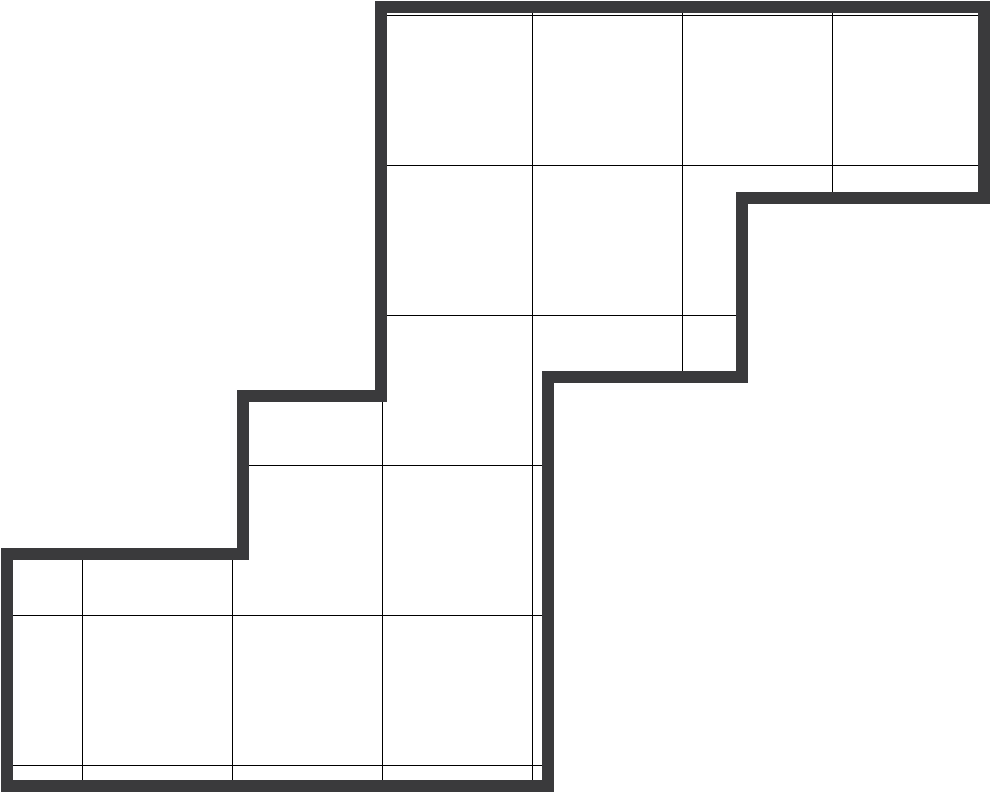

3D Rotations





Likewise, the bottom three blocks protrude to the left of the middle.
We can easily visualize the shape based on this information. When we compare it to the available options, we see that the main features are reversed.
Text



3D Rotations





We can easily visualize the shape based on this information. When we compare it to the available options, we see that the main features are reversed.
Text


This can only happen if the object is either reflected or rotated completely around the y-axis.
The question specifies that the answer should be a rotation, not a reflection. We must therefore visualize the original object rotated 180° around the y-axis.

3D Rotations





Text

The question specifies that the answer should be a rotation, not a reflection. We must therefore visualize the original object rotated 180° around the y-axis.
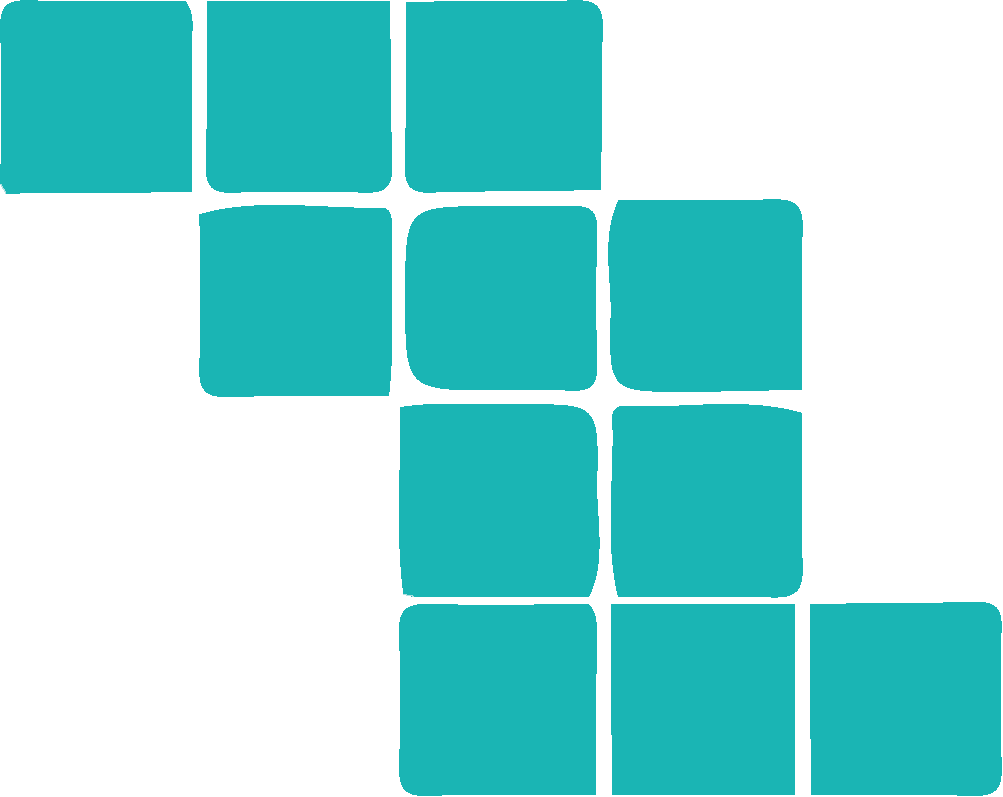
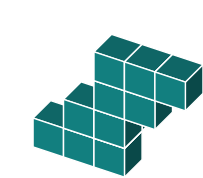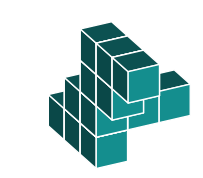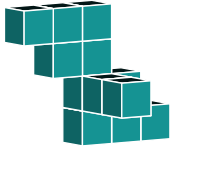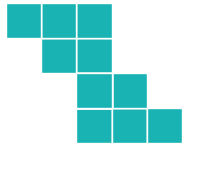
Counting the blocks row by row, we can see that the original has 3, 2, 2, 3 blocks.

3D Rotations





Text

Counting the blocks row by row, we can see that the original has 3, 2, 2, 3 blocks.
This rules out options a, c and d. They do not have the same 3, 2, 2, 3 block combination.

3D Rotations





Text

This rules out options a, c and d. They do not have the same 3, 2, 2, 3 block combination.

Studying the two remaining options, we see that the difference is how the second-from-top row is aligned. In option b, the two blocks do not "point" in the expected direction.
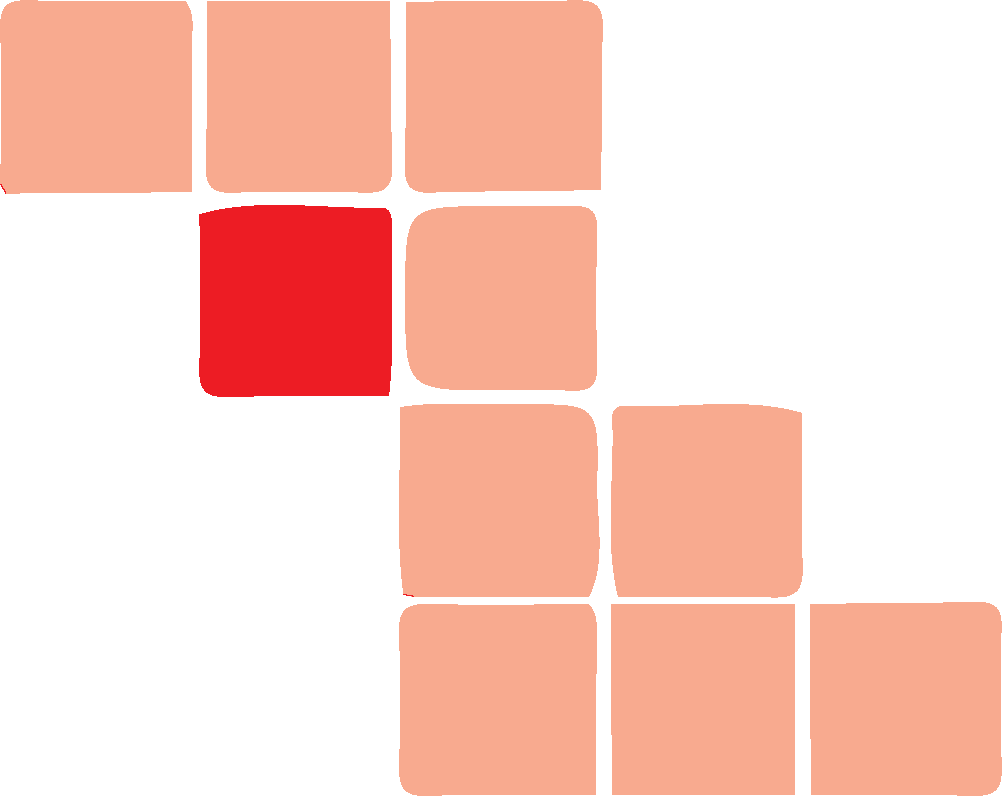
3D Rotations




Text

The correct answer is e.

Visualise the Movement: Imagine holding the 3D shape in your hands. Rotate or flip it mentally to match the question. Practice with physical models or online 3D tools if needed.
3D rotations and reflections
Visualise the Movement: Imagine holding the 3D shape in your hands. Rotate or flip it mentally to match the question. Practice with physical models or online 3D tools if needed.
3D rotations and reflections
Focus on Key Features: Look for distinct elements like patterns, colours, or shapes on the surface of the object. Track how these features move or change during rotation or reflection.
Visualise the Movement: Imagine holding the 3D shape in your hands. Rotate or flip it mentally to match the question. Practice with physical models or online 3D tools if needed.
3D rotations and reflections
Focus on Key Features: Look for distinct elements like patterns, colours, or shapes on the surface of the object. Track how these features move or change during rotation or reflection.
Understand Axes of Rotation: Rotations can occur around different axes (X, Y, Z). Recognise whether the shape is turning vertically, horizontally, or diagonally.
3D rotations and reflections
Understand Axes of Rotation: Rotations can occur around different axes (X, Y, Z). Recognise whether the shape is turning vertically, horizontally, or diagonally.
Reflections and Symmetry: For mirror reflections, think about how the shape would look in a mirror. Identify lines or planes of symmetry to predict the flipped shape.
3D rotations and reflections
Understand Axes of Rotation: Rotations can occur around different axes (X, Y, Z). Recognise whether the shape is turning vertically, horizontally, or diagonally.
Reflections and Symmetry: For mirror reflections, think about how the shape would look in a mirror. Identify lines or planes of symmetry to predict the flipped shape.
Eliminate Wrong Options: Use process of elimination to rule out options that don’t match the shape’s size, orientation, or features after rotation/reflection.
3D rotations and reflections
Eliminate Wrong Options: Use process of elimination to rule out options that don’t match the shape’s size, orientation, or features after rotation/reflection.
Practise Timed Exercises: Speed and accuracy are key in 11+ exams. Regularly practise rotation and reflection questions within time limits to improve performance.

Well done! You should now have a very good understanding of 3D objects in non-verbal reasoning. NVR requires a lot of practice, however, so the next step is to get going with some of our NVR mock tests. Don't despair if your first scores aren't as good as you had hoped. The key to NVR tests is familiarity with the question types. Keep practicing and you will notice that you get a little bit better and a little bit faster each time.