Similarities and Pattern Identification
2D Shape rotations and reflections
2D shapes can be rotated in one axis.

2D Shape rotations and reflections
2D shapes can be rotated in one axis.

2D Shape rotations and reflections
2D shapes can be rotated in one axis.

Text
This makes them easier to recognise in different rotations than 3D objects which can be rotated around 3 axis.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
When we rotate a 2D object, we rotate it around a point on the x-y plane.
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
A special type of "rotation" is mirroring, where an image is reflected along a line.
2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
A special type of "rotation" is mirroring, where an image is reflected along a line.

As you can see, the result of reflecting an image is different from rotating it.

2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
Here we are rotating around a central point.
But we could also rotate around any other point on the x-y plane.
A special type of "rotation" is mirroring, where an image is reflected along a line.

As you can see, the result of reflecting an image is different from rotating it.

2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
A special type of "rotation" is mirroring, where an image is reflected along a line.

As you can see, the result of reflecting an image is different from rotating it.

2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
A special type of "rotation" is mirroring, where an image is reflected along a line.
Objects can be reflected across any line of reflection.

2D Shape rotations and reflections

Text
A special type of "rotation" is mirroring, where an image is reflected along a line.
Objects can be reflected across any line of reflection.

2D Shape rotations and reflections


Text
A special type of "rotation" is mirroring, where an image is reflected along a line.
Objects can be reflected across any line of reflection.

As you can see, this image changes appearance as it is reflected. Some objects, however, look the same when reflected along certain lines.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Text
Objects can be reflected across any line of reflection.
As you can see, this image changes appearance as it is reflected. Some objects, however, look the same when reflected along certain lines.
Let's see how lines of reflection affects this square.


2D Shape rotations and reflections
Text
As you can see, this image changes appearance as it is reflected. Some objects, however, look the same when reflected along certain lines.
Let's see how lines of reflection affects this square.
As you can see, it keeps the same shape when reflected along a vertical middle line of reflection.


2D Shape rotations and reflections
Text
As you can see, this image changes appearance as it is reflected. Some objects, however, look the same when reflected along certain lines.
Let's see how lines of reflection affects this square.
As you can see, it keeps the same shape when reflected along a vertical middle line of reflection.


...and a horizontal line of reflection.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Text
As you can see, this image changes appearance as it is reflected. Some objects, however, look the same when reflected along certain lines.
Let's see how lines of reflection affects this square.
As you can see, it keeps the same shape when reflected along a vertical middle line of reflection.
...and a horizontal line of reflection.
...and even if reflected along central diagonal lines.
2D Shape rotations and reflections


Text
As you can see, it keeps the same shape when reflected along a vertical middle line of reflection.
...and a horizontal line of reflection.
...and even if reflected along central diagonal lines.
We call these lines lines of symmetry and a square will have four of them.

2D Shape rotations and reflections
Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
How many lines of symmetry can you spot in this pentagram?


Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
How many lines of symmetry can you spot in this pentagram?


The first one is quite easy to spot: down the middle.
Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections


But there are more. Another line runs from the inner vertices to the points.
How many lines of symmetry can you spot in this pentagram?
The first one is quite easy to spot: down the middle.

Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
But there are more. Another line runs from the inner vertices to the points.
If we rotate the star you can see that this is in fact just another line through the middle.

Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
If we rotate the star you can see that this is in fact just another line through the middle.

We can repeat this rotation five times.
Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
If we rotate the star you can see that this is in fact just another line through the middle.

We can repeat this rotation five times.
Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
If we rotate the star you can see that this is in fact just another line through the middle.

We can repeat this rotation five times.
Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
If we rotate the star you can see that this is in fact just another line through the middle.

We can repeat this rotation five times.
Each of these lines will reflect the pentagram without changing its appearance. Thus, a pentagram has 5 lines of symmetry.
Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Circles are unique because they possess an infinite number of lines of symmetry. Any line that passes through the centre of the circle will serve as a line of symmetry.
Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Circles are unique because they possess an infinite number of lines of symmetry. Any line that passes through the centre of the circle will serve as a line of symmetry.
Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Circles are unique because they possess an infinite number of lines of symmetry. Any line that passes through the centre of the circle will serve as a line of symmetry.
However, if the line does not go through the centre of the circle it is not a line of symmetry.

Text
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Circles are unique as they have an unlimited number of lines of symmetry. Any line that goes through the centre of the circle will be a line of symmetry.
If the line does not pass through the center of the circle, it is not a line of symmetry.


2D Shape rotations and reflections
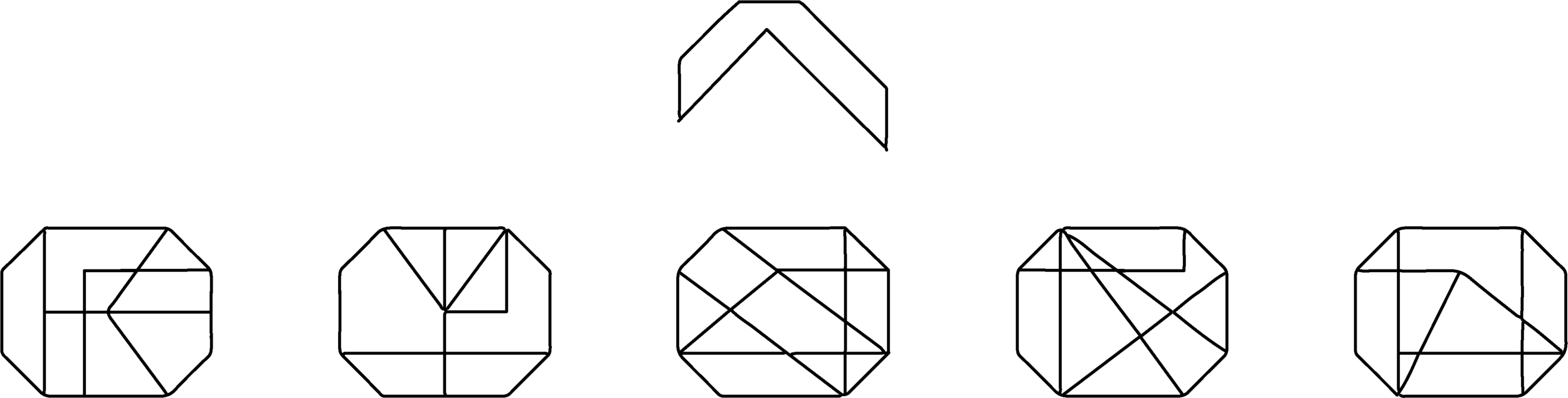
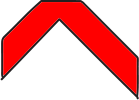
You may be asked to find shapes that are scaled and/or rotated and hidden within other shapes.
Can you identify the top shape concealed within one of the answer choices?
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may be asked to find shapes that are scaled and/or rotated and hidden within other shapes.
Can you identify the top shape concealed within one of the answer choices?


Be prepared to come across several red herrings designed to mislead you.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may be asked to find shapes that are scaled and/or rotated and hidden within other shapes.
Can you identify the top shape concealed within one of the answer choices?


Be prepared to come across several red herrings designed to mislead you.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may be asked to find shapes that are scaled and/or rotated and hidden within other shapes.
Can you identify the top shape concealed within one of the answer choices?


Be prepared to come across several red herrings designed to mislead you.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may be asked to find shapes that are scaled and/or rotated and hidden within other shapes.


Be prepared to come across several red herrings designed to mislead you.
The correct answer is c
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may also be asked to identify shapes that have been mirrored.
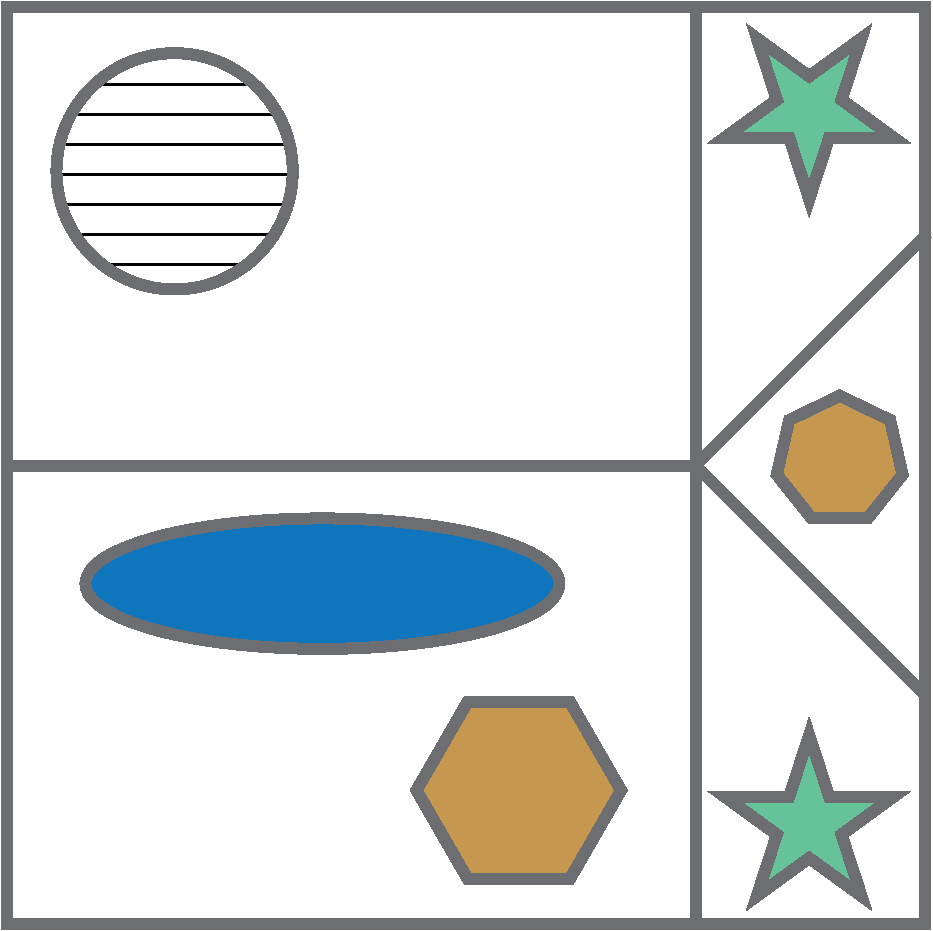
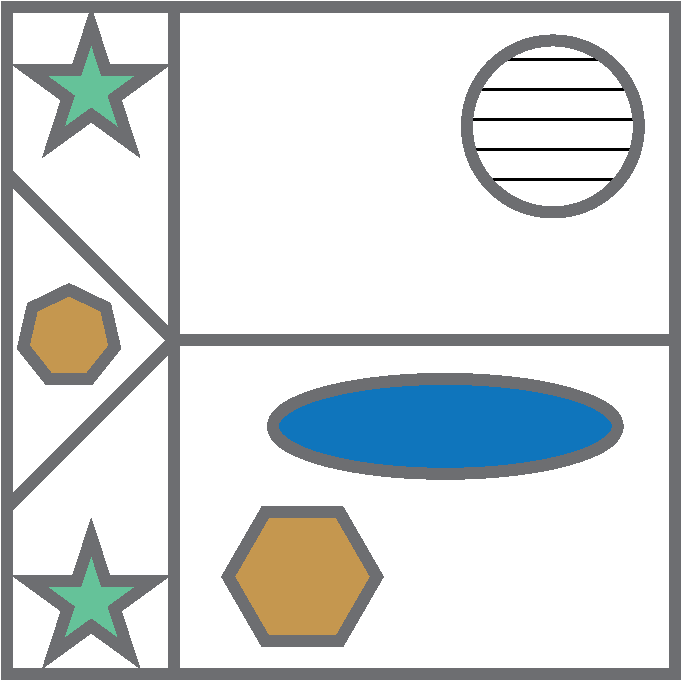
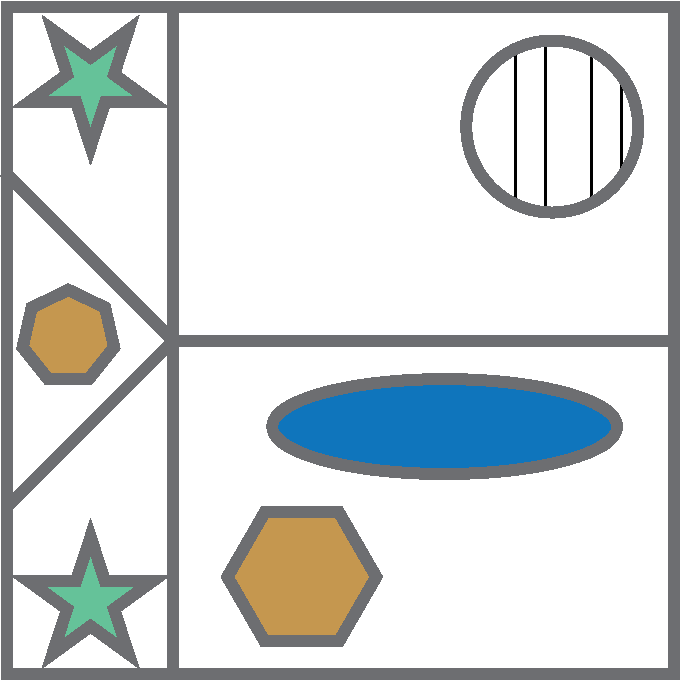
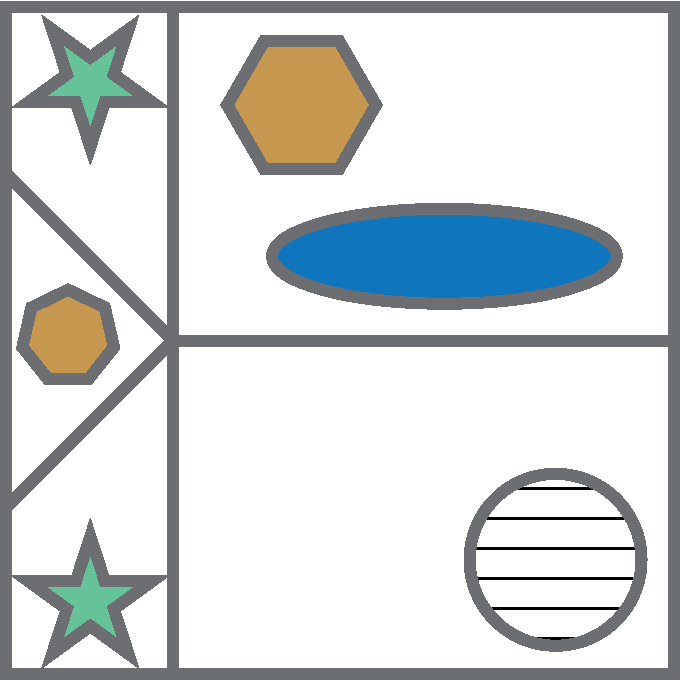
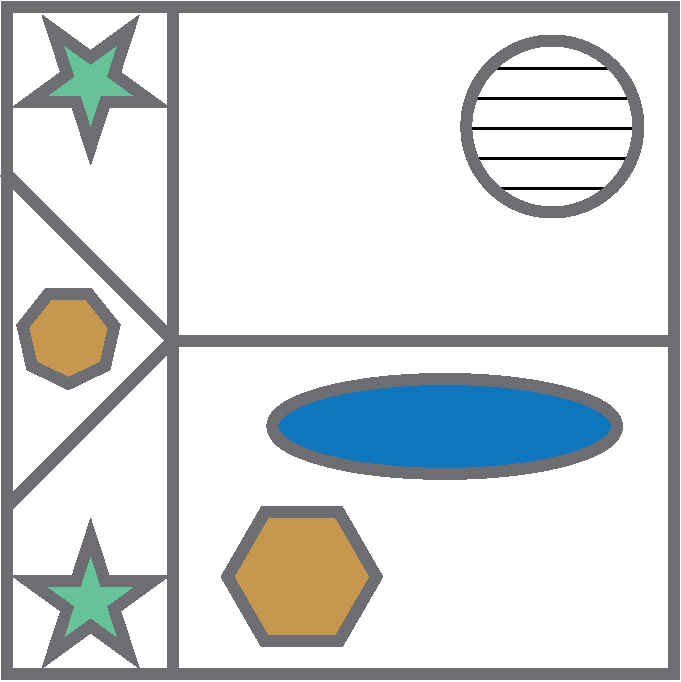
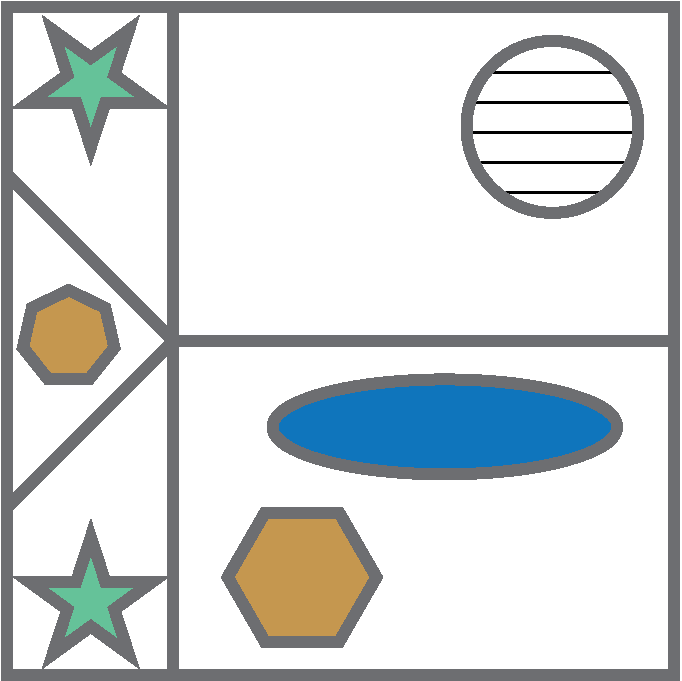
Can you determine which of these options is the correct mirror image of the original on the left?
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may also be asked to identify shapes that have been mirrored.






The top star is rotated incorrectly. It seems to be pointing upwards and out of the square, whereas in the original, the two stars point towards each other.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may also be asked to identify shapes that have been mirrored.






The lines of the circle are vertical when they should be horizontal.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may also be asked to identify shapes that have been mirrored.






The shape is reflected across a vertical line, but the top and bottom sections have switched places. This can only occur if the rotation happens along a horizontal plane.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may also be asked to identify shapes that have been mirrored.






This is very subtle, but the shape in the triangle is incorrectly rotated.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
You may also be asked to identify shapes that have been mirrored.






Shape e is correct. It is a proper reflection of the original shape.
Rotation vs. Reflection: Always determine whether you are working with a rotation or a reflection before you start solving.
Beware of Red Herrings: Some shapes may appear similar in orientation. Be sure to check for subtle differences in size or position. Begin by examining the overall shape, then confirm by looking at finer details, such as edges.
Visualize or Make a Rough Sketch: When comparing shapes, visualize what you are searching for in broad outlines. If permitted, it can be helpful to roughly sketch the expected outlines on notepaper.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Tips and Hints for 2D Shape Rotations
Rotation vs. Reflection: Always determine whether you are working with a rotation or a reflection before you start solving.
Beware of Red Herrings: Some shapes may appear similar in orientation. Be sure to check for subtle differences in size or position. Begin by examining the overall shape, then confirm by looking at finer details, such as edges.
Visualize or Make a Rough Sketch: When comparing shapes, visualize what you are searching for in broad outlines. If permitted, it can be helpful to roughly sketch the expected outlines on notepaper.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Tips and Hints for 2D Shape Rotations
Rotation vs. Reflection: Always determine whether you are working with a rotation or a reflection before you start solving.
Beware of Red Herrings: Some shapes may appear similar in orientation. Be sure to check for subtle differences in size or position. Begin by examining the overall shape, then confirm by looking at finer details, such as edges.
Visualize or Make a Rough Sketch: When comparing shapes, visualize what you are searching for in broad outlines. If permitted, it can be helpful to roughly sketch the expected outlines on notepaper.
2D Shape rotations and reflections
Tips and Hints for 2D Shape Rotations

Well done! You should now have a very good understanding of rotations and reflections in non-verbal reasoning. NVR requires a lot of practice, however, so the next step is to get going with some of our NVR mock tests. Don't despair if your first scores aren't as good as you had hoped. The key to NVR tests is familiarity with the question types. Keep practicing and you will notice that you get a little bit better and a little bit faster each time.